As electronic energy systems become more resilient and efficient, digitalization in the power sector grows ever more prominent. In fact, global investment in digital electricity infrastructure has grown by around 20% annually since 2014. However, increased energy system digitalization often faces more complex cyber security challenges. Many cyber threat groups steal data and exploit vulnerabilities in the energy sector for financial or political gain. To counter this threat, while still capitalizing on its benefits, the United States partnered with ASEAN cities to advance the field of grid digitalization and cybersecurity.
Two pilot cities within the ASEAN Smart Cities Network were selected to develop realistic smart city plans and policies. Each city collected and analyzed data, accounting for evidence-based planning processes, in order to create and implement options for more fully integrated renewables and heightened cybersecurity within utility systems. The project also aimed to improve coordination across city departments and between the cities and local stakeholders. The two pilot cities selected for this project were Bangkok, Thailand and Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia.
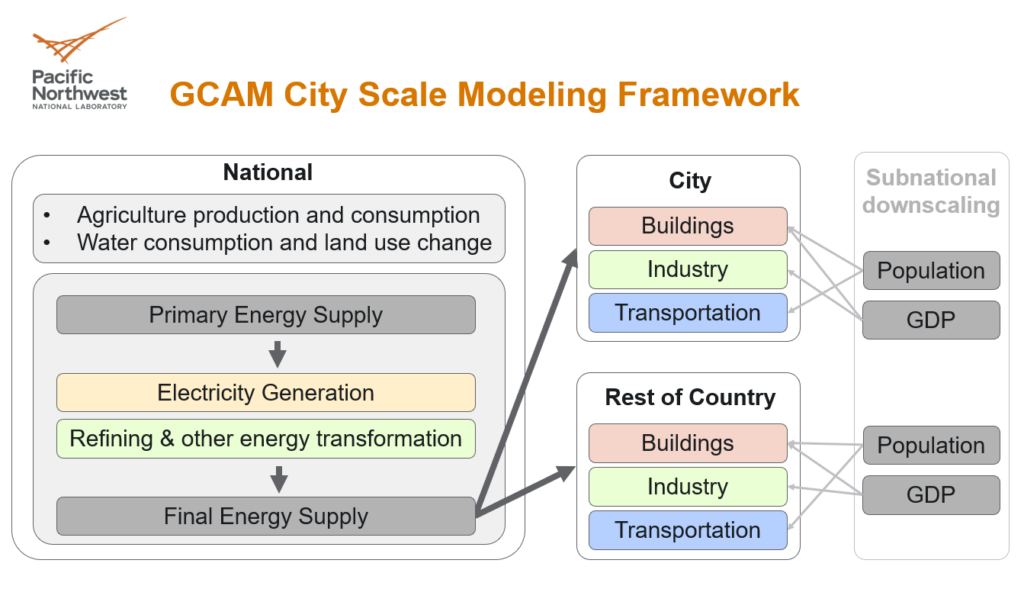
The State Department Bureau of Energy Resources and Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL) implemented the project and prepared analyses on key energy and environmental trends to inform local planning efforts. The Global Change Assessment Model (GCAM)‘s integrated analysis supported modeling and training in the pilot cities and enabling officials to outline smart city recommendations and implementation plans.
What is the Global Change Assessment Model (GCAM)?
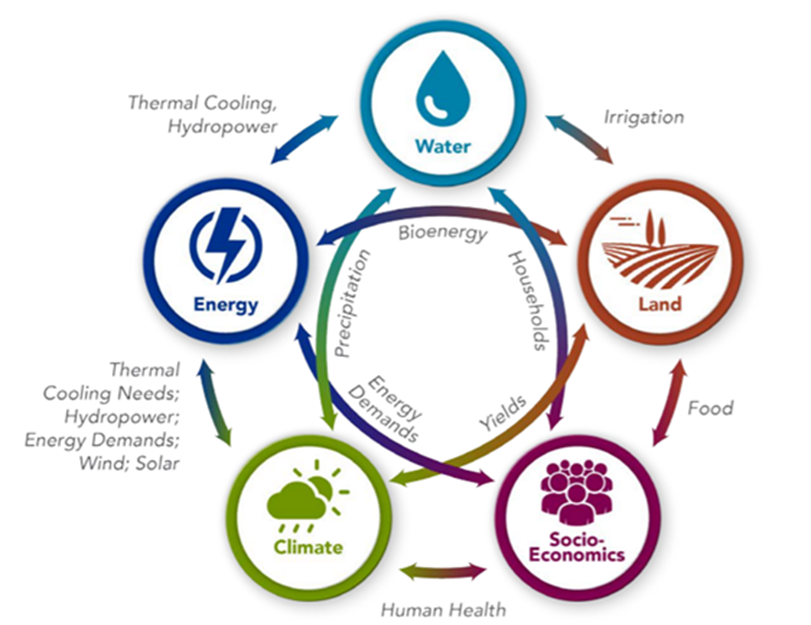
“GCAM is a market equilibrium model with a global scope and operates from 1990 to 2100 in five-year time steps. It can be used to examine, for example, how changes in population, income, or technology cost might alter crop production, energy demand, and water withdrawals, or how changes in one region’s demand for energy affect energy, water, and land in other regions.
GCAM has been developed at Pacific Northwest National Laboratory for over 30 years and is now a freely available community model and documented online. The team at JGCRI is comprised of economists, engineers, energy experts, forest ecologists, agricultural scientists, and climate system scientists who develop the model and apply it to a range of science and policy questions. The team works closely with Earth system and ecosystem modelers to integrate the human decision components of GCAM into their analyses.”
Source: https://gcims.pnnl.gov/modeling/gcam-global-change-analysis-model
 U.S.-ASEAN Smart Cities Partnership
U.S.-ASEAN Smart Cities Partnership

